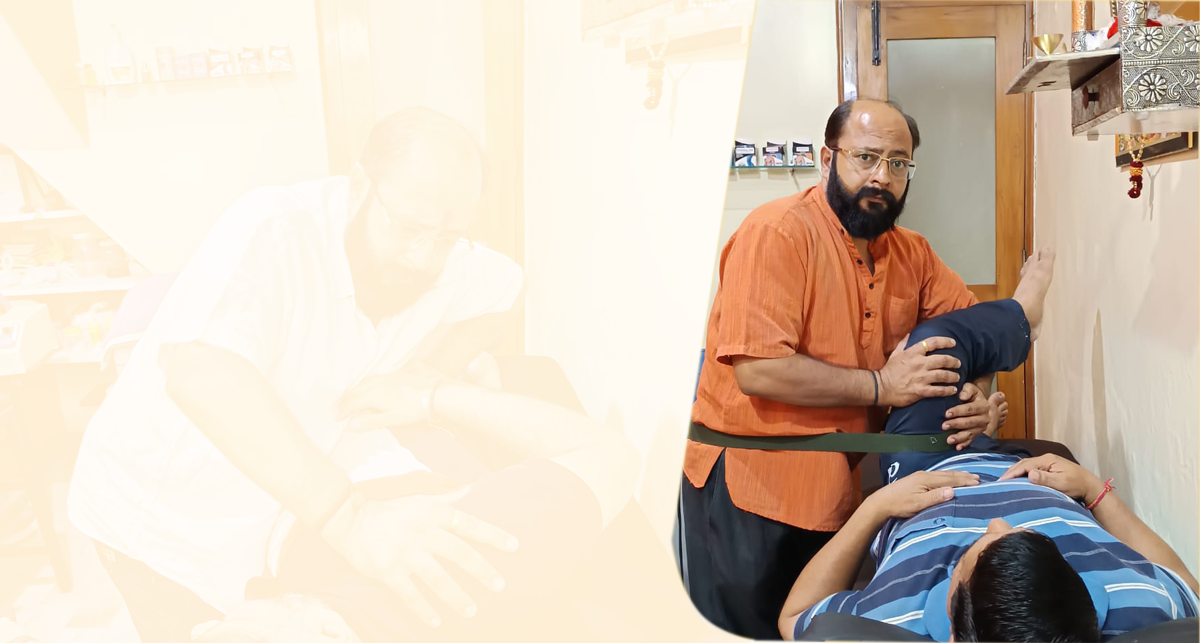
Post-stroke physiotherapy is a crucial part of rehabilitation for individuals who have experienced a stroke. Let’s explore how we, at Shri SiyaRam Clinic, can help and what it involves:
How Can Physiotherapy Help After a Stroke?
Movement Improvement: A stroke can cause weakness or paralysis on one side of your body, affecting movement and everyday activities. At Shri SiyaRam Clinic Our Physiotherapists help you learn to move effectively, regain strength, and improve mobility.
Treatment of Specific Problems: Our Physiotherapists address various issues, including muscle stiffness, spasticity, movement difficulties, balance problems, joint pain, and changes in sensation.
Multi-Disciplinary Approach: Physiotherapists at ShriSiyaRam Clinic collaborate with occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, doctors, nurses, and social workers as part of the stroke team. This multi-disciplinary approach ensures comprehensive care.
Neuroplasticity and Recovery:
After a stroke, the brain cannot grow new cells to replace damaged ones. However, it can reorganize undamaged cells through a process called neuroplasticity.
Physiotherapy guides this relearning process, helping you regain function and movement.
Types of Movement Problems Treated by Physiotherapists at Shri SiyaRam Clinic:
Weakness or Paralysis: Physiotherapists at Shri SiyaRam Clinic focuses on strengthening weakened muscles and improving coordination.
Sensory Changes: Our Physiotherapists address heavy limbs, numbness, and pins and needles.
Balance Issues: Exercises and techniques enhance balance.
Joint Pain and Stiffness: At Shri SiyaRam Clinic we help manage joint discomfort.
Spasticity: Muscle spasms can be addressed through targeted interventions.
When Does Physiotherapy Begin?
As early as 24 hours after a stroke, you’ll be encouraged to get up and move. Early physiotherapy aims to prevent complications and support recovery.
Later, it focuses on enabling you to perform essential activities like getting out of bed or participating in sports.
Rehabilitation Exercises:
Stretching and Range of Motion: These exercises improve flexibility, prevent contractures, and decrease the risk of injury. Hold each stretch for at least 10-30 seconds.
Functional Task-Specific Training: Practicing activities relevant to daily life while standing or walking.
Balance Training: Overground walking and obstacle courses challenge standing balance.
Lower Limb Strengthening: Exercises to strengthen leg muscles.
Ankle-Foot Orthosis (AFO): Consider using an AFO if needed.
Remember, progress may take time, but consistent effort pays off. If your exercises ever decide to play hide-and-seek, just gently coax them back—they’ll come around!